Domain Name System
 The key part of a Uniform Resource Locator (URL), https://blog.tinyray.com/dns-intro for example, is the name of the server holding the resource, "blog.tinyray.com" given the example, which is usually called host. The name of server, or hostname, is an easily memorized alphabet string to help human beings. It however needs to be translated into a complex numerical string, IP4 or IP6, which describes the physical address of the server in the internet. A system of hostnames and IP addresses, called Domain Name System (DNS), is therefore required to support the translation.
The key part of a Uniform Resource Locator (URL), https://blog.tinyray.com/dns-intro for example, is the name of the server holding the resource, "blog.tinyray.com" given the example, which is usually called host. The name of server, or hostname, is an easily memorized alphabet string to help human beings. It however needs to be translated into a complex numerical string, IP4 or IP6, which describes the physical address of the server in the internet. A system of hostnames and IP addresses, called Domain Name System (DNS), is therefore required to support the translation.
DNS is a hierarchical distributed naming system for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network. It associates various kinds of information with domain names assigned to each of the participating entities. Most prominently, it translates easily memorized domain names to the numerical IP addresses needed for the purpose of locating computer services and devices worldwide. DNS is an essential component of the functionality of the Internet.
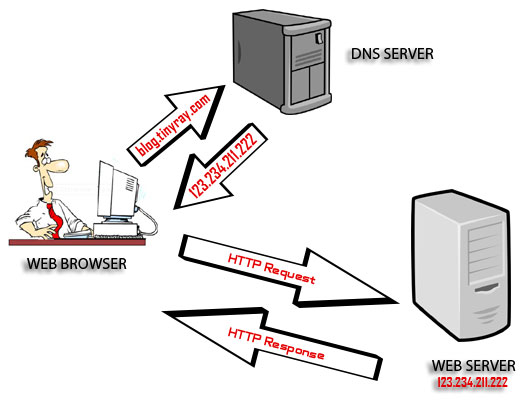
DNS works like a phone book and is supported by a system of domain name service (DNS*) servers, each of which performs hostname-to-IP translation for a substructure, or a zone, in the DNS hierarchical layout. Unlike a phone book, DNS can be quickly updated, allowing a resource's location on the internet to change without affecting the end users, who continue to use the same hostname.
Each DNS server can be either a master server or a slave server. A master server is a server that stores the original (master) copies of all zone records. A slave server uses an automatic updating mechanism of the DNS protocol in communication with its master to maintain an identical copy of the master records.
A set of DNS servers has to be assigned for every DNS zone. An NS record of addresses of the DNS servers in such a set must be stored in the parent zone and the servers themselves for self-reference. As an end user, you take advantage of the DNS whenever you use an URL, just like typing https://blog.tinyray.com/dns-intro to visit this article's page. Translation of "blog.tinyray.com" results in leading you to a server in a hosting center or to my home PC. It is amazing but not a magic. It makes more fun for people making and/or using the internet resources. Thank you for reading this article. (*) DNS can be referred as Domain Name System, Domain Name Service or Domain Name Server depending on the context.